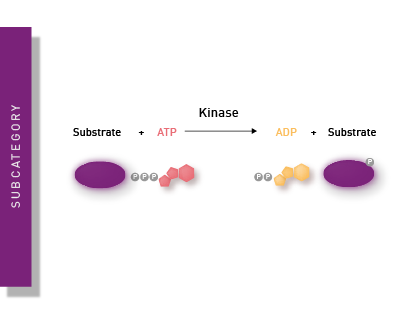
Measuring thousands of wells in minutes for drug screening
An essential part of the early phase of drug discovery is screening libraries of compounds in order to detect potential ‘hits’ which interact with a therapeutic target. Common targets include membrane proteins such as GPCRs, thereby especially orphan GPCRs, ion channels as well as kinases. Compounds acting on a therapeutic target have to be identified out of libraries of thousands to millions of compounds, making automation of the process using microplate readers essential.
Screens are mainly conducted in 384 and 1536 well plates to minimize reaction volumes per sample. Speed and sensitivity are key requirements for screens as is assay quality. A 1536 well microplate needs to be measured in seconds, maximally a few minutes. Furthermore, the fast measurement of 10 µl or even lower volume samples needs to be very precise and stable to clearly identify hits from a vast number of compounds. In addition, the reader needs to be reliable, as errors occurring during a screen result in repetitions, loss of time, reagents and consequently money.
BMG LATBECH’s multi-mode microplate readers have market leading performance ensuring hits can be reliably detected at low volumes and at the fastest speeds. This not only enables the highest throughput but also allows rapid cycle times in kinetic assays required for studying binding kinetics and on/off rates.
The PHERAstar FSX masters all these requirements in all detection modes, and also meets supports the changing needs of screening facilities, making it popular in screening facilities. For screening assay development and testing, the CLARIOstar Plus is the perfect addition to develop and characterize an assay before transitioning to high throughput.
Take a look at the links below to find out more about our instruments and how they have been used by drug screeners.


Receptors
Resources
Search our resources section for information about specific applications, literature citations, videos, blog articles and many other publications. Many of the resources provided are associated with current and previous instrument models and versions.

Identification of peptide ligands for orphan GPCRs by measuring Ca2+-induced luminescence in transfected cells
You are planning to inject living cells with a microplate reader? Read here how the VANTAstar with magnetic stirrer and heater keeps your cells happy and in suspension till the moment of injection.
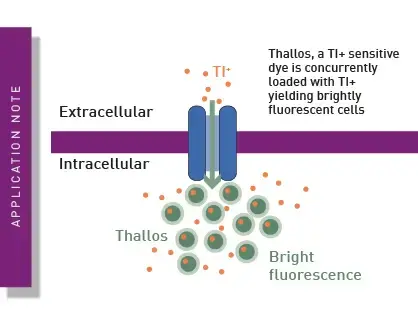
Adaptation of a potassium channel assay to enable easier high throughput screening
Plan to analyse ion channels with a thallium-sensitive dye but don't have an imager? No problem! This adapted assay allows high-throughput detection of ion channel activity on a microplate reader.
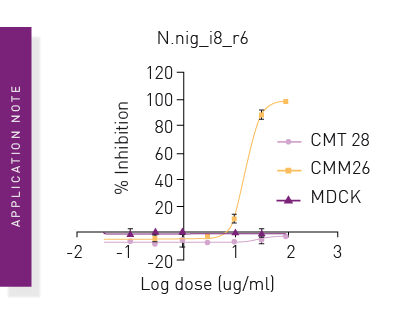
Resazurin Cell Viability Assay for the Discovery of Selective Cytotoxic Compounds in Canine Mammary Cancer Research
Snake venom has a very bad image. But it’s not all bad - If you would like to read about the useful functions of snake venoms as an anti-cancer treatment click here.
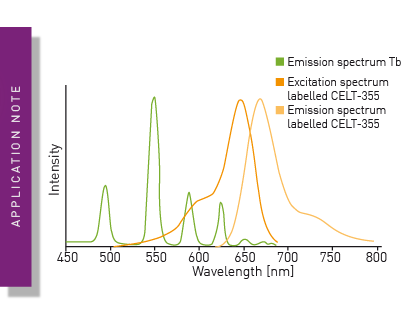
Differential binding of ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol derivatives to type 1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1)
Looking for alternative acceptor fluorophores in TR-FRET attempts? Read here how CELT-335 was successfully used in a Cannabinoid competition binding assay at CB1.
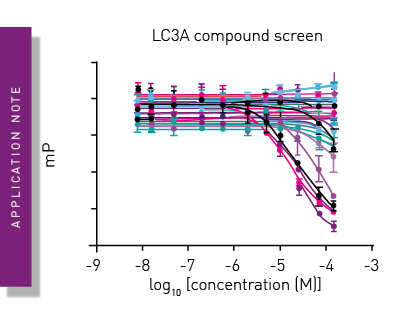
High-throughput screening and hit validation with a fluorescence polarization assay
Read here, how a fluorescence polarization-based interaction assay on the PHERAstar FSX can be used to reduce sample volumes, cost, and time-requirements for high-throughput screening.
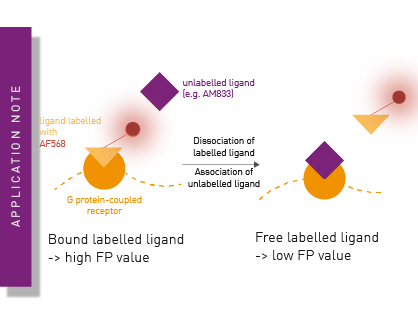
Competition assay using Fluorescence Polarization to determine the Residence Times for Calcitonin and AMYR agonist, AM833
Inform yourself here about the benefits of an alternative to (TR-)FRET-/BRET-based competition assays using FP for the determination of kon and koff of ligand/receptor interaction.
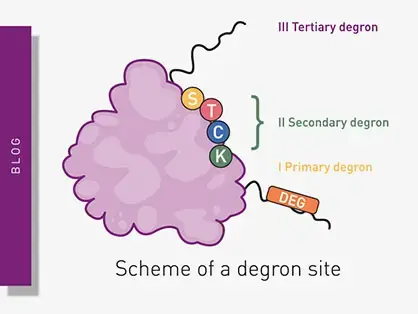
The Roles of Degrons in Targeted Protein Degradation
Degrons are specific sequences of amino acids or structural motifs within a protein that are important for targeted protein degradation. Find out how microplate readers can advance research into natural and engineered degrons.
Gene reporter assays
Gene reporter assays are sensitive and specific tools to study the regulation of gene expression. Learn about the different options available, their uses, and the benefits of running these types of assays on microplate readers.
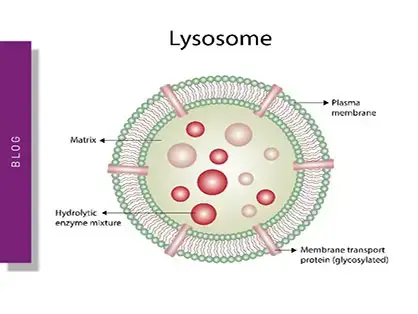
Targeted protein degradation and next-generation degraders
Innovation for targeted protein degradation and next-generation degraders is gathering pace. This blog introduces some of the different approaches that act via the lysosome or proteasome.
Cell-based protein degrader assays for microplates
The choice of assay for targeted protein degradation studies is crucial. But what is the preferred assay and detection technology for your specific research needs and microplate reader?
Molecular glues: new solutions for undruggable proteins
Molecular glues are small molecules that help target unwanted proteins for destruction by the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Find out how microplate readers can advance molecular glue research.
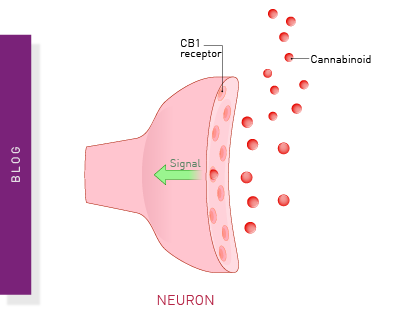
Cannabinoid receptor ligands as templates for drug discovery
Cannabinoids offer exciting opportunities to target diverse diseases with unmet needs. Learn how microplate readers can help improve our understanding of drug screening and drug signaling events to help advance cannabinoid research.
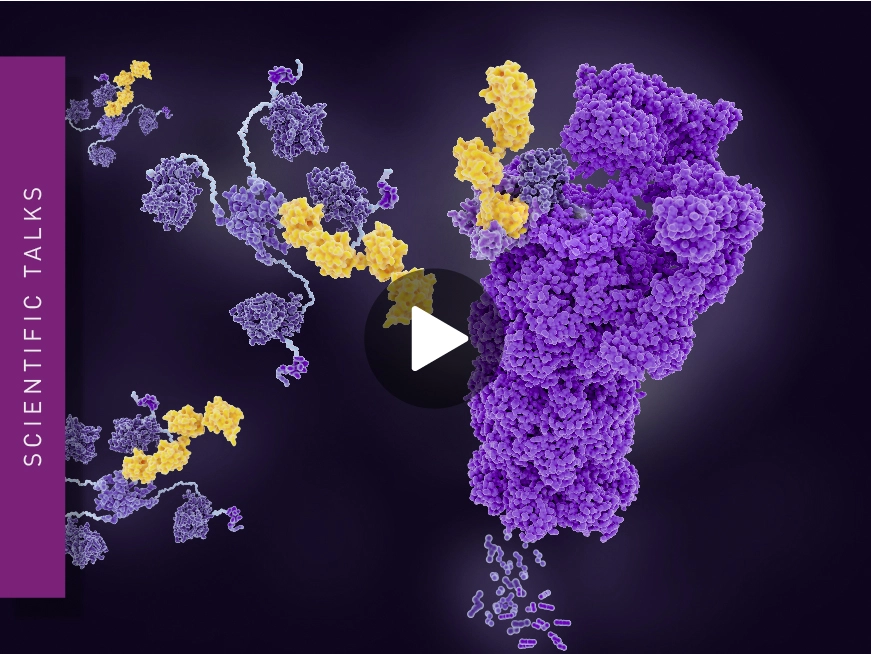
Live cell systems for degrader evaluation
Martin Schwalm discusses measuring PROTAC-induced degradation, ternary complex formation kinetics and stability, and shows a complete pipeline using live cells.
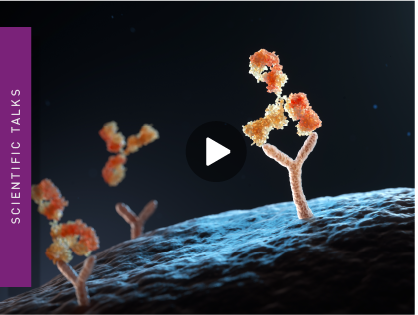
Targeting the type 1 cholecystokinin receptor to screen for novel obesity treatments
Development of functional, binding and multiplex assays targeting the type 1 cholecystokinin receptor to screen for potential new compounds against obesity.
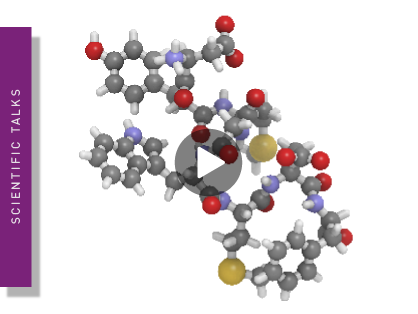
Binding affinity determination on microplate readers
Binding affinity is an important parameter in drug discovery. Find out, how microplate readers can be used for binding affinity determination and the advantages they offer.
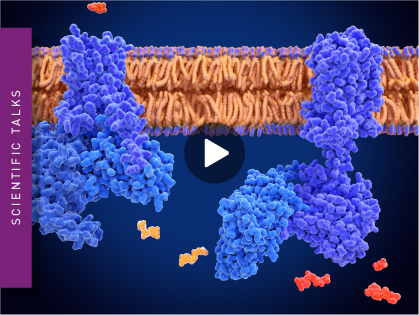
Using the TRUPATH BRET platform to analyse GPCR biased agonism
TRUPATH is a BRET-based platform that enables to monitor discrete GPCR-G protein coupling and can facilitate the discovery of drugs biased towards desired G protein effectors.
Current microplate-based interaction assays for drug discovery
Protein-protein interaction is the key in physiological processes - and likewise many diseases. Learn here about possible approaches to study interactions in drug screening using NanoBRET and TR-FRET.
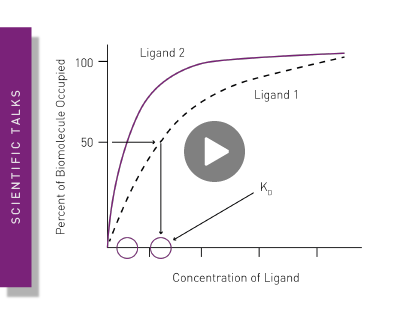
Kinetics in Drug Discovery
Martin Redhead, group leader at UCB, discusses the use and impact of kinetic binding methods across the drug discovery pipeline.

Tackling rare and neglected cancers with advanced screening
Charlotte Walsh-Tripp from Cancer Research Horizons discusses their approach to cancer research, focusing on challenging targets and utilizing advanced screening technologies.

Pioneering Pre-Clinical Drug Discovery with Advanced Assays
Discover how Excellerate Bioscience leverages advanced assays and PHERAstar technology to revolutionize pre-clinical drug discovery and pharmacology services.

CLARIOstar and PHERAstar support a variety of biological assays in early drug discovery with flexibility and precision
Nick Bland’s benefits: Z´ of 0.9 in HTS studies and the flexibility to run different assays.

Building a bridge between organoid research and drug discovery
Elad Katz founder of Navigate Precision Biology established a 384-well based organoid platform and runs his assays with the PHERAstar.

The benefits of studying opioid, cannabinoid, terpenoid, and 5HT receptor agonists
Dr Marina Junqueira Santiago discusses the potential benefits of studying opioid, cannabinoid, terpenoid, and 5HT receptor agonists.

Targeted protein degradation – next-generation therapeutics
Helen Harrison, Director of Screening at Amphista Therapeutics, discusses targeted protein degradation and the discovery of drugs in this area.

PHERAstar FSX
Powerful and most sensitive HTS plate reader

CLARIOstar Plus
Most flexible Plate Reader for Assay Development

NEPHELOstar Plus
Microplate nephelometer for light-scattering and turbidity measurements



