Introduction
Diabetes mellitus is characterized by disruption of normal metabolism that stems from resistance to insulin or poor insulin secretion1. In 2014 it was reported that nearly 10% of the U.S. population suffers from diabetes and that 90% of diabetes cases are type-2 diabetes2,3. Because of the high prevalence of this disease and the equally high financial burden associated with treatment it remains a focus to find new therapeutics.
Secretion of physiologically active insulin is regulated at multiple steps as outlined in Figure 1. Each of these steps represents a chance for therapeutic intervention4.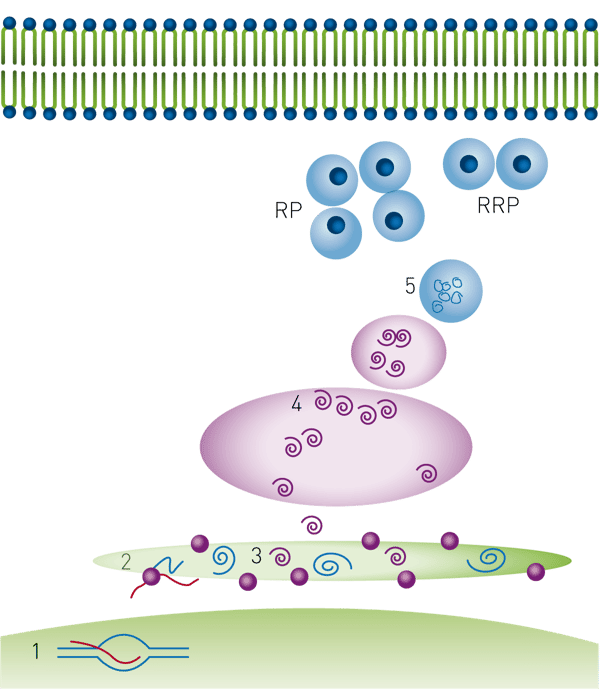
Assay Principle
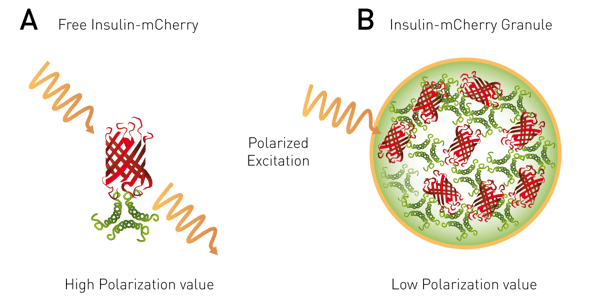
This application note describes a high throughput screening compatible cell based assay that uses a preproinsulin-mCherry (PPI-mCherry) system. The application exploits the fact that when a fluorophore is at a high local concentration FRET can occur between the same type of fluorophores. This phenomenon is called homoFRET (HF). Furthermore if polarized light is applied as the excitation light it will become randomized as the HF occurs between adjacent fluorophores. It was reasoned that a HF-FP approach would be suitable to monitor the extent of packing of mature insulin into dense core granules (Figure 2).
Materials & Methods
- 384-well black/clear bottom plates (NUNC #152029)
- Rat insulinoma (INS-1) cells were donated by Christopher Newgard at Duke University
- Preproinsulin (PPI) mCherry Reporter Construct was made in Dr. Brenman’s lab at UNC
- 1,280 molecule FDA-approved drug set (Prestwick Chemical Library)
- 502 purified natural products (Enzo Life Sciences)
- PHERAstar microplate reader from BMG LABTECH
PHERAstar Instrument Settings
| Measurement type: | Fluorescence Polarization |
| Measurement mode: | End point |
| Optic module: | FP(590-50/675-50/675-50) |
| Gain: | adjusted prior to test run |
| Target mP value: | 400 |
| Focal height: | 7.2 |
| Flashes / well: | 200 |
Results & Discussion
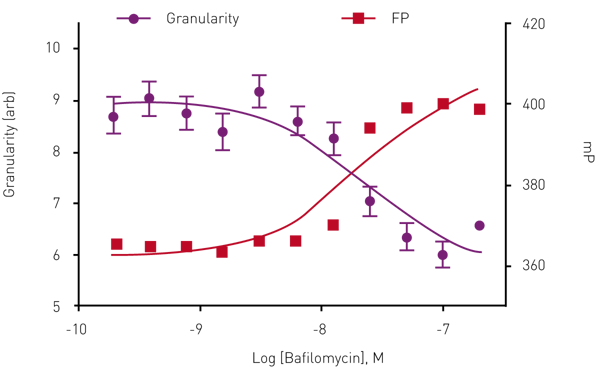
To validate the homoFRET-FP approach cells were treated with Bafilomycin, a vacuolar-type H+ ATPase (V-ATPase) inhibitor known to block vacuole maturation and thus block insulin granule formation (Figure 3). The results show that increasing concentrations of Bafilomycin result in an increase in mP value correlating with decreased granule formation.
Figure 5 shows the representative confirmation of the three hits from the pilot screen. Overall the screen ex-hibited a hit rate of 1.4 % and a confirmation rate of 36.4 %.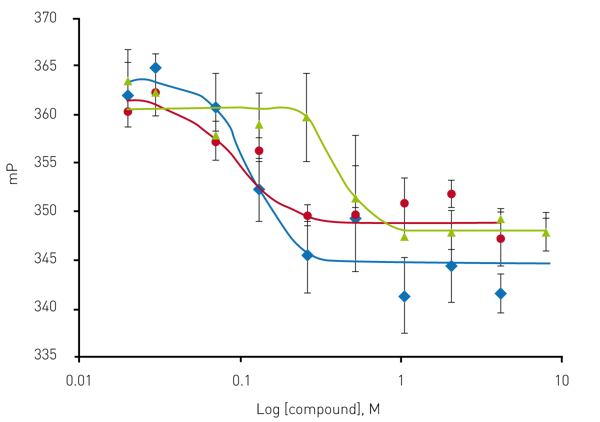
Conclusion
These results establish a novel cell-based FP biosensor to identify compounds that modify insulin granule packaging. This technology may serve as a new method for assessing protein-protein interactions in live cell systems.
References
- Rorsman P et al. (2000) The Cell Physiology of Biphasic Insulin Secretion.
News Physiol. Sci. 15:72-77. - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) (2014) National Diabetes Statistics Report.
- Huang CJ et al. (2007) High expression rates of human islet amyloid polypeptide induce endoplasmic reticulum stress mediated beta-cell apoptosis, a characteristic of humans with type 2 but not type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 56(8): 2016-2027.
- Yi NY et al. (2015) Development of a Cell-Based Fluorescence Polarization Biosensor Using Preproinsulin to Identify Compounds That Alter Insulin Granule Dynamics. Assay Drug. Dev. Technol. 13(9): 558-569.

![Fig. 4: FP data from pilot screen. Scatter plot of 1,782 test compounds (green) [hits (green stars)], negative control (DMSO red) and positive control (Bafilomycin blue). Arrows indicate Anti- mycin A1 is selected from both libraries.](https://www.bmglabtech.com/hs-fs/hubfs/Webseite/5_Resources/App%20Notes/4_App%20Notes%20250-299/AN297-Fig4.webp?width=600&name=AN297-Fig4.webp)